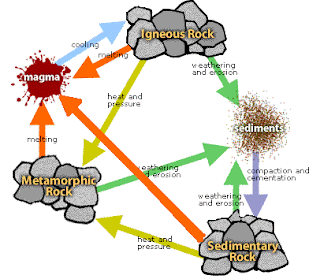
Rock Cycle
Rocks change constantly from one
type to another. First the magma uplifts by the force of
gases through a mountain, which is mostly referred as Volcano. When these
molten rocks travel outside, they are named as lava. Because of the
different temperature of inside and outside of earth, the lava solidifies
and become solid, known as Igneous Rock. By weathering and erosion,
the rocks break down in small sediments. Later, these sediments are
pushed together and become a new rock, known as Sedimentary Rock. As the
rocks travel downwards by the layers of the earth, they heat up and pressure
acts on them, making layers and producing another kind of Metamorphic Rock.
The rocks keep travelling downwards, and finally meet up with magma, which is
located at the most bottom of the layers. And so on, the rock forming cycle
keeps working.
Rocks
Metamorphic Rock: Rocks
formed by heat and pressure.
Magma: Molted
rocks inside the earth.
Lava: Molted
rocks outside the earth.
Solidification: The
process by which lava cools down and becomes solid.
Igneous Rock: Rocks
formed when lava is cooled down and solidifying.
Weathering: When
rocks are broken down by storms etc.
Erosion: When
rocks are moved from the surface by winds etc.
Sediment: Small rocks
broke down by weathering and erosion.
Compaction: Process
by which sediments come together.
Cementation: Process
by which sediments are glued together.
Sedimentary Rock: Rocks
formed when compaction and cementation takes place with sediments.
Rock Types
Igneous Intrusive
Rock: Igneous Rocks that are
formed inside of the earth.
Igneous Extrusive
Rock: Igneous Rocks that are formed outside of the earth.
Sedimentary Clastic
Rock: Sedimentary rocks formed when little fragments are glued together.
Sedimentary
Crystalline Rock: Sedimentary Rocks formed when minerals and evaporation.
Sedimentary
Bioclastic Rock: Sedimentary Rocks formed when left over of dead organisms
are glued together.
Metamorphic Foliated
Rock: Metamorphic Rocks formed
as layers.
Metamorphic
Non-Foliated Rock: Metamorphic Rocks formed without layers.

No comments:
Post a Comment